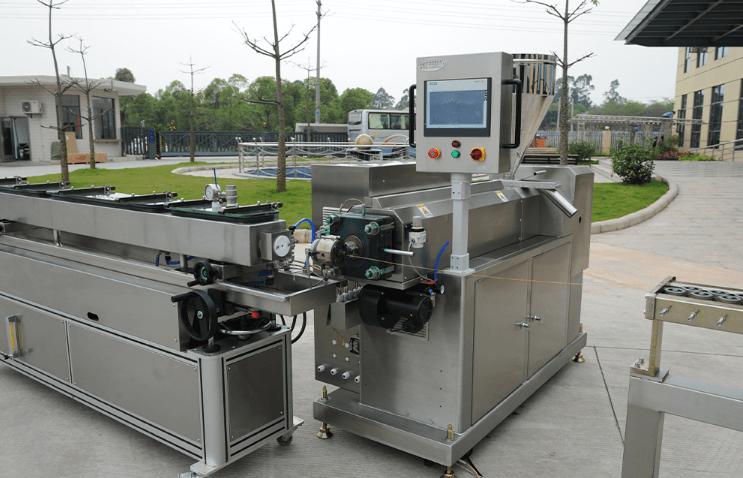
Ultimate Guide to HDPE Catheter Extruders
Catheter extrusion is a critical aspect of medical device manufacturing, particularly when it comes to catheters made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE). Understanding catheter extrusion, the role of HDPE in medical devices, and the comparison between HDPE and PVC can help medical professionals and manufacturers make informed decisions. In this ultimate guide, we will explore these topics in detail.
What is Catheter Extrusion?
Catheter extrusion refers to a situation where a catheter, a flexible tube-like medical device, becomes partially or completely displaced from its intended position within the body. The term "extrusion" implies that the catheter has been pushed out or has exited from its original placement site.
Catheters are commonly used in various medical procedures to deliver fluids, medications, or contrast agents, or to assist in the drainage of fluids from the body. They can be inserted into blood vessels, the urinary tract, or other body cavities. However, in some cases, the catheter may inadvertently move out of position due to factors such as patient movement, improper securing, or mechanical forces acting on the catheter.
When catheter extrusion occurs, it can result in complications and may require prompt medical attention. The consequences can vary depending on the specific situation and the location of the catheter. For instance, if a urinary catheter becomes extruded, it may cause urine leakage or urinary tract infections. In the case of vascular catheters, extrusion can lead to bleeding or damage to blood vessels.
Preventing catheter extrusion involves proper insertion techniques, securement methods, and regular monitoring of the catheter's position. Healthcare professionals are trained to minimize the risk of catheter displacement and promptly address any signs of extrusion.
It is important to note that while I strive to provide accurate and up-to-date information, it's always best to consult with a healthcare professional for specific medical advice or concerns.
Catheters are commonly used in various medical procedures to deliver fluids, medications, or contrast agents, or to assist in the drainage of fluids from the body. They can be inserted into blood vessels, the urinary tract, or other body cavities. However, in some cases, the catheter may inadvertently move out of position due to factors such as patient movement, improper securing, or mechanical forces acting on the catheter.
When catheter extrusion occurs, it can result in complications and may require prompt medical attention. The consequences can vary depending on the specific situation and the location of the catheter. For instance, if a urinary catheter becomes extruded, it may cause urine leakage or urinary tract infections. In the case of vascular catheters, extrusion can lead to bleeding or damage to blood vessels.
Preventing catheter extrusion involves proper insertion techniques, securement methods, and regular monitoring of the catheter's position. Healthcare professionals are trained to minimize the risk of catheter displacement and promptly address any signs of extrusion.
It is important to note that while I strive to provide accurate and up-to-date information, it's always best to consult with a healthcare professional for specific medical advice or concerns.
What is HDPE for Medical Devices?
HDPE stands for high-density polyethylene, which is a type of thermoplastic polymer. It is a versatile material known for its durability, strength, and resistance to chemicals. HDPE is widely used in various industries, including the medical field.
In the context of medical devices, HDPE is commonly employed due to its favorable characteristics. Here are some key attributes of HDPE for medical devices:
●Biocompatibility: HDPE is considered biocompatible, meaning it is well-tolerated by the human body and does not elicit a significant immune response. This makes it suitable for applications involving direct or indirect contact with biological tissues or fluids.
●Sterilization compatibility: HDPE can withstand different sterilization methods, including gamma radiation, ethylene oxide (ETO) gas, and autoclaving. This property is crucial for medical devices that need to be sterilized before use to ensure patient safety.
●Chemical resistance: HDPE is resistant to many chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents. This resistance is beneficial in medical devices that come into contact with various substances during their use, such as containers for storing chemicals or solutions.
●Flexibility and strength: HDPE offers a balance of flexibility and strength, making it suitable for applications where both properties are important. It can be molded into different shapes and sizes while maintaining its structural integrity.
●Ease of fabrication: HDPE is relatively easy to fabricate, allowing for efficient manufacturing processes. It can be extruded, injection-molded, or blow-molded into complex shapes, enabling the production of intricate medical devices.
●Some examples of medical devices that may utilize HDPE include containers for storing and transporting medical supplies, components of surgical instruments, tubing for fluid transfer, orthopedic implants, and prosthetic components.
It's worth noting that while HDPE has many advantageous properties for medical devices, the specific choice of materials depends on the intended use, regulatory requirements, and other factors. Therefore, it's essential to consult with experts in the field, such as medical device engineers or manufacturers, to determine the most suitable materials for specific applications.
In the context of medical devices, HDPE is commonly employed due to its favorable characteristics. Here are some key attributes of HDPE for medical devices:
●Biocompatibility: HDPE is considered biocompatible, meaning it is well-tolerated by the human body and does not elicit a significant immune response. This makes it suitable for applications involving direct or indirect contact with biological tissues or fluids.
●Sterilization compatibility: HDPE can withstand different sterilization methods, including gamma radiation, ethylene oxide (ETO) gas, and autoclaving. This property is crucial for medical devices that need to be sterilized before use to ensure patient safety.
●Chemical resistance: HDPE is resistant to many chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents. This resistance is beneficial in medical devices that come into contact with various substances during their use, such as containers for storing chemicals or solutions.
●Flexibility and strength: HDPE offers a balance of flexibility and strength, making it suitable for applications where both properties are important. It can be molded into different shapes and sizes while maintaining its structural integrity.
●Ease of fabrication: HDPE is relatively easy to fabricate, allowing for efficient manufacturing processes. It can be extruded, injection-molded, or blow-molded into complex shapes, enabling the production of intricate medical devices.
●Some examples of medical devices that may utilize HDPE include containers for storing and transporting medical supplies, components of surgical instruments, tubing for fluid transfer, orthopedic implants, and prosthetic components.
It's worth noting that while HDPE has many advantageous properties for medical devices, the specific choice of materials depends on the intended use, regulatory requirements, and other factors. Therefore, it's essential to consult with experts in the field, such as medical device engineers or manufacturers, to determine the most suitable materials for specific applications.
Is HDPE Better than PVC?
Determining whether HDPE (high-density polyethylene) is better than PVC (polyvinyl chloride) depends on the specific context and application. Both materials have their own strengths and weaknesses, and the choice between them often depends on factors such as the intended use, regulatory requirements, cost considerations, and environmental impact. Here are some key points to consider:
●Physical properties: HDPE and PVC have different physical properties. HDPE is known for its high strength, impact resistance, and flexibility. It can withstand a wide range of temperatures and is resistant to chemicals. PVC, on the other hand, is rigid, has good tensile strength, and is resistant to flame, UV radiation, and weathering.
●Chemical resistance: HDPE has excellent resistance to chemicals, acids, and bases, making it suitable for applications involving exposure to various substances. PVC also has good chemical resistance, although it may not be as resistant to certain solvents or hydrocarbons compared to HDPE.
●Installation and maintenance: PVC is often chosen for its ease of installation and low maintenance requirements. It can be easily cut, joined, and glued using common techniques. HDPE, while still manageable, may require specialized joining methods such as heat fusion or mechanical connections.
●Environmental considerations: HDPE is considered more environmentally friendly compared to PVC. HDPE is recyclable and has a lower carbon footprint during production. PVC, on the other hand, raises concerns due to the presence of chlorine in its composition and the potential release of toxic chemicals during manufacturing and incineration.
●Applications: Both HDPE and PVC find applications in various industries, including construction, agriculture, packaging, and healthcare. HDPE is commonly used in water and gas distribution systems, sewage pipes, and packaging containers. PVC is often used for electrical conduits, window frames, flooring, and medical tubing.
In summary, the choice between HDPE and PVC depends on the specific requirements of the application, including factors such as mechanical strength, chemical resistance, flexibility, installation method, and environmental considerations. Consulting with experts, such as engineers or manufacturers familiar with the specific industry and application, can help determine the most suitable material for a given project.
●Physical properties: HDPE and PVC have different physical properties. HDPE is known for its high strength, impact resistance, and flexibility. It can withstand a wide range of temperatures and is resistant to chemicals. PVC, on the other hand, is rigid, has good tensile strength, and is resistant to flame, UV radiation, and weathering.
●Chemical resistance: HDPE has excellent resistance to chemicals, acids, and bases, making it suitable for applications involving exposure to various substances. PVC also has good chemical resistance, although it may not be as resistant to certain solvents or hydrocarbons compared to HDPE.
●Installation and maintenance: PVC is often chosen for its ease of installation and low maintenance requirements. It can be easily cut, joined, and glued using common techniques. HDPE, while still manageable, may require specialized joining methods such as heat fusion or mechanical connections.
●Environmental considerations: HDPE is considered more environmentally friendly compared to PVC. HDPE is recyclable and has a lower carbon footprint during production. PVC, on the other hand, raises concerns due to the presence of chlorine in its composition and the potential release of toxic chemicals during manufacturing and incineration.
●Applications: Both HDPE and PVC find applications in various industries, including construction, agriculture, packaging, and healthcare. HDPE is commonly used in water and gas distribution systems, sewage pipes, and packaging containers. PVC is often used for electrical conduits, window frames, flooring, and medical tubing.
In summary, the choice between HDPE and PVC depends on the specific requirements of the application, including factors such as mechanical strength, chemical resistance, flexibility, installation method, and environmental considerations. Consulting with experts, such as engineers or manufacturers familiar with the specific industry and application, can help determine the most suitable material for a given project.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of catheter extrusion, the advantages of HDPE for medical devices, and the comparison between HDPE and PVC enables medical professionals and manufacturers to make informed decisions. With this ultimate guide, you now have the knowledge to navigate the world of HDPE catheter extruders and select the most appropriate materials for your medical device needs.